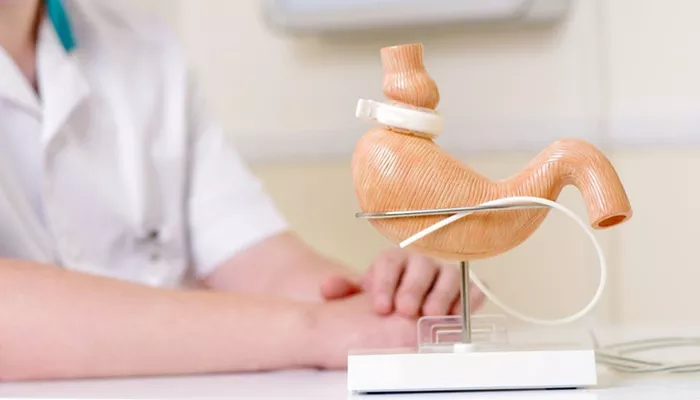
Gastric bypass surgery, commonly known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is a well-established weight loss surgery designed for individuals struggling with obesity. It involves altering the digestive system to limit food intake and reduce the amount of calories and nutrients absorbed by the body. This procedure is typically recommended for individuals who have not had success with traditional weight loss methods, such as dieting and exercise, and have a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or more, or a BMI of 35 or more with obesity-related health conditions.
This article provides a detailed overview of gastric bypass surgery, its procedure, benefits, and potential risks, ensuring that readers fully understand what this surgery entails before considering it as a weight loss solution.
Understanding Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery is a bariatric procedure that changes the way the digestive system works. The procedure not only reduces the stomach size but also reroutes the small intestine to limit food absorption. This results in significant weight loss and can improve or resolve obesity-related health issues like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea.
The Purpose of Gastric Bypass Surgery
The primary goal of gastric bypass surgery is weight loss. The surgery works by:
Restricting the amount of food that can be eaten.
Decreasing the number of calories and nutrients absorbed by the body.
This combination of restriction and malabsorption leads to a caloric deficit, which, over time, results in weight loss. In addition to its weight loss benefits, gastric bypass surgery also has significant metabolic effects, such as improved insulin sensitivity.
The Gastric Bypass Procedure
The gastric bypass procedure is performed under general anesthesia and typically takes between 2 to 4 hours. There are two main steps involved:
Stomach Reduction:
The surgeon divides the stomach into two sections. The upper part of the stomach is reduced to a small pouch, about the size of a walnut, which limits the amount of food the stomach can hold. The remaining portion of the stomach is bypassed.
Rerouting the Small Intestine:
The small intestine is then rerouted to connect to the small stomach pouch. The bypassed part of the stomach and a portion of the small intestine are no longer involved in digestion. This limits the absorption of calories and nutrients.
The surgery can be performed using either open surgery (a large incision) or laparoscopic surgery (small incisions with the help of a camera). Laparoscopic surgery is less invasive, with a faster recovery time.
Benefits of Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery offers several benefits, especially for individuals dealing with severe obesity and obesity-related health conditions.
Significant Weight Loss
One of the most notable benefits of gastric bypass surgery is substantial weight loss. On average, patients can expect to lose about 60 to 80 percent of their excess weight within the first two years after the surgery. This weight loss can greatly improve physical appearance, mobility, and overall quality of life.
Improvement in Health Conditions
For individuals suffering from obesity-related health issues, gastric bypass can lead to dramatic improvements or even complete resolution of conditions such as:
Type 2 diabetes: Many patients experience a reduction in blood sugar levels and some may be able to stop using diabetes medications after surgery.
Sleep apnea: Weight loss after gastric bypass can reduce or eliminate symptoms of sleep apnea.
Hypertension (high blood pressure): Weight loss can also help lower blood pressure, potentially reducing the need for medications.
Enhanced Psychological Well-being
Obesity often leads to mental health challenges such as depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. Significant weight loss following gastric bypass surgery can improve self-image and boost confidence. Many patients report a greater sense of well-being and satisfaction with their physical appearance.
Increased Life Expectancy
By improving obesity-related conditions and promoting weight loss, gastric bypass surgery can contribute to an increased life expectancy. Studies have shown that individuals who undergo bariatric surgery often experience a lower risk of premature death due to obesity-related complications.
Risks and Potential Complications
While gastric bypass surgery can offer life-changing benefits, it is not without risks. As with any major surgery, there are potential complications that patients need to be aware of.
Short-term Risks
Some of the short-term risks associated with gastric bypass surgery include:
Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection at the incision sites or within the abdominal cavity.
Blood clots: Blood clots, particularly in the legs (deep vein thrombosis), can form after surgery and may travel to the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
Leaking: The newly created connections between the stomach and small intestine can sometimes leak, which may require further treatment.
Nausea and vomiting: Post-surgery, some patients experience nausea or vomiting, especially if they eat too much or too quickly.
Long-term Risks
In the long term, patients may face several potential complications, including:
Nutrient deficiencies:
Because gastric bypass surgery reduces the absorption of nutrients, patients are at risk of developing deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, such as iron, calcium, and vitamin B12. Lifelong supplementation is typically required.
Dumping syndrome:
This condition occurs when food moves too quickly from the stomach into the small intestine, leading to symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, and dizziness.
Gallstones:
Rapid weight loss can increase the risk of gallstones. In some cases, a gallbladder removal surgery may be needed.
Bowel obstruction:
Scar tissue from surgery can sometimes cause a blockage in the small intestine, which may require further treatment.
Psychological and Emotional Considerations
While gastric bypass surgery can improve physical health, it can also have psychological effects. Patients may experience changes in their eating behaviors and emotional well-being. Support from mental health professionals and dietitians is often essential during the recovery process.
Post-Surgery Lifestyle Changes
Successful long-term weight loss following gastric bypass surgery requires significant lifestyle changes. Patients must adopt a healthy diet, engage in regular physical activity, and commit to lifelong medical follow-up.
Dietary Changes
Immediately after surgery, patients are placed on a liquid diet and gradually progress to solid foods. The types and quantities of foods are strictly controlled to prevent discomfort and ensure proper digestion. Foods high in fat and sugar are typically avoided to prevent dumping syndrome. A typical post-surgery diet includes:
Small meals: Patients must eat small portions throughout the day, as the new stomach pouch can only hold a small amount of food.
High-protein foods: Protein is prioritized to aid in healing and maintain muscle mass.
Vitamin and mineral supplements: Patients will need to take supplements to prevent deficiencies.
Exercise
After recovery, patients are encouraged to engage in regular physical activity to help maintain weight loss and improve overall health. Exercise should be gradually introduced, starting with light activities such as walking, and progressing to more vigorous exercises as tolerated.
Follow-up Care
Regular follow-up visits with healthcare providers are essential to monitor progress, address any complications, and adjust medications or supplements as needed. Blood tests are performed to check for nutritional deficiencies, and lifestyle counseling is provided to help patients stay on track.
Conclusion
Gastric bypass surgery is a powerful tool for weight loss, offering significant health benefits for individuals suffering from severe obesity. By reducing the stomach size and rerouting the small intestine, gastric bypass not only leads to weight loss but also helps improve or resolve obesity-related health conditions. However, it is important to recognize that the surgery requires permanent lifestyle changes, including dietary adjustments, physical activity, and ongoing medical support.
For those who meet the criteria and are committed to the necessary lifestyle changes, gastric bypass can be a life-altering procedure that improves both physical and mental well-being. If you are considering this surgery, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to assess your individual circumstances and determine whether gastric bypass is the right option for you.